About the tool
It is common to repeat this code in several places:
navigate('/auth/login')
This is not scalable and is problematic since on many occasions a certain path can change due to customer request or project needs, and the result is changing a line of code in several parts of the code, which can easily cause bugs.
Finally, this new Navigation system was created, where all the application's routes are concentrated in one variable, making changes faster and safer.
Other important details are:
- The way to write the route was created to completely mirror mobile navigation so that the developer does not feel so much difference between platforms.
- The navigate function has full typescript support, so when the developer needs to write, he will have a list of available routes:
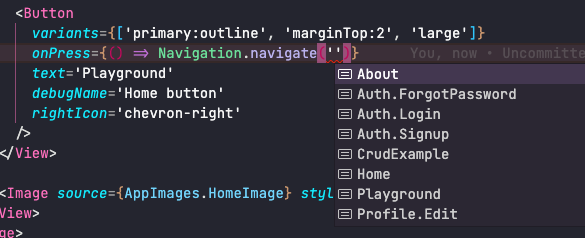
How to use
Create a file that will contain the application routes and the declaration of the navigation.
Example:
import { Navigation, Navigator } from '@codeleap/web'import { navigate } from 'gatsby'// App routes// For you to add a new route or change one, you must follow the same pattern as the others.const routes = {Home: '/',Profile: {Edit: 'profile/edit',},Auth: {Login: 'auth/login',Signup: 'auth/signup',ForgotPassword: 'auth/forgot',},About: 'about',Playground: 'playground',Crud: {Example: 'crud',View: 'crud/{{id}}'}} as const// Function that will be used for navigation.const navigator: Navigator = (path, options) => navigate(path, options)export const navigation = new Navigation(routes, navigator)
Dynamic parameter inference
You may notice that the Crud.View example route has an id surrounded by double curly braces {{}}, these are the route parameters.
You can define any parameter for the route, for example:
const routes = {Page: {Example: 'page/{{pageId}}/{{otherId}}/view'}}
In this situation, you are declaring that the Page.Example route requires the pageId and otherId parameters. From this, TypeScript will dynamically infer that the route needs these parameters.
It's important that the parameter is surrounded by curly braces {{}} for inference to work correctly and later be able to replace the values to form the route path.
When you call the navigation function, using navigation.navigate, TypeScript will assist you in this way:
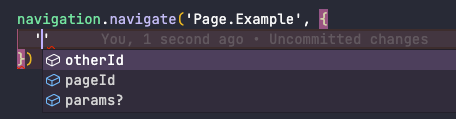
Parameters
The Navigation class receives three parameters:
Routes
The first parameter is an object with all the routes of the application.
The navigator
The second parameter is a function of type Navigator that will be used to navigate, it receives the path and an object with options, if any.
Configurations
The third parameter is the configurations.
const navigation = new Navigation(routes, navigator, {historyEnabled: true,getMetadata: () => ({})})
- historyEnabled: Enable or disable history, the default value is false.
- getMetadata: Function that should return an object that will be inserted along with the history.
History
The Navigation class keeps track of the navigation history. It stores information about each navigation action, including the path, origin, date, metadata, and additional information.
You can access the navigation history as follows:
const appHistory = navigation.history
Methods
isCurrentRoute
Checks if the user is on a certain route based on the parameters passed:
- route: Route that will be used to direct.
- routeParams: Parameters that will be applied to the route.
- exact: Accurate path checking - default false.
Example:
const isHome = navigation.isCurrentRoute('Home')
getPath
Get the path from the route.
Example:
const homePath = navigation.getPath('Home')
getPathWithParams
Get the path from the route and route params.
Example:
const homePath = navigation.getPathWithParams('Home', { id: 'abc' })
goBack
Navigate to the previous page. If history is enabled, the penultimate record will be used, otherwise the browser's own api with history.back().
Example:
navigation.goBack()
wipeHistory
Clear history data.
Example:
navigation.wipeHistory()
navigate
Navigate between the app using the route system with dynamic parameters and query parameters. The arguments that can be passed are:
- route: Route that will be used to direct.
- options: Route parameters (marked by
{{}}in route), which will be automatically shown if they exist, and route queryParams can also be passed through the "params" property.
Example:
navigation.navigate('Home', {id: 'abc',params: {title: 'Page example'}})