At a glance
This documentation is under review
📘 Infrastructure Overview
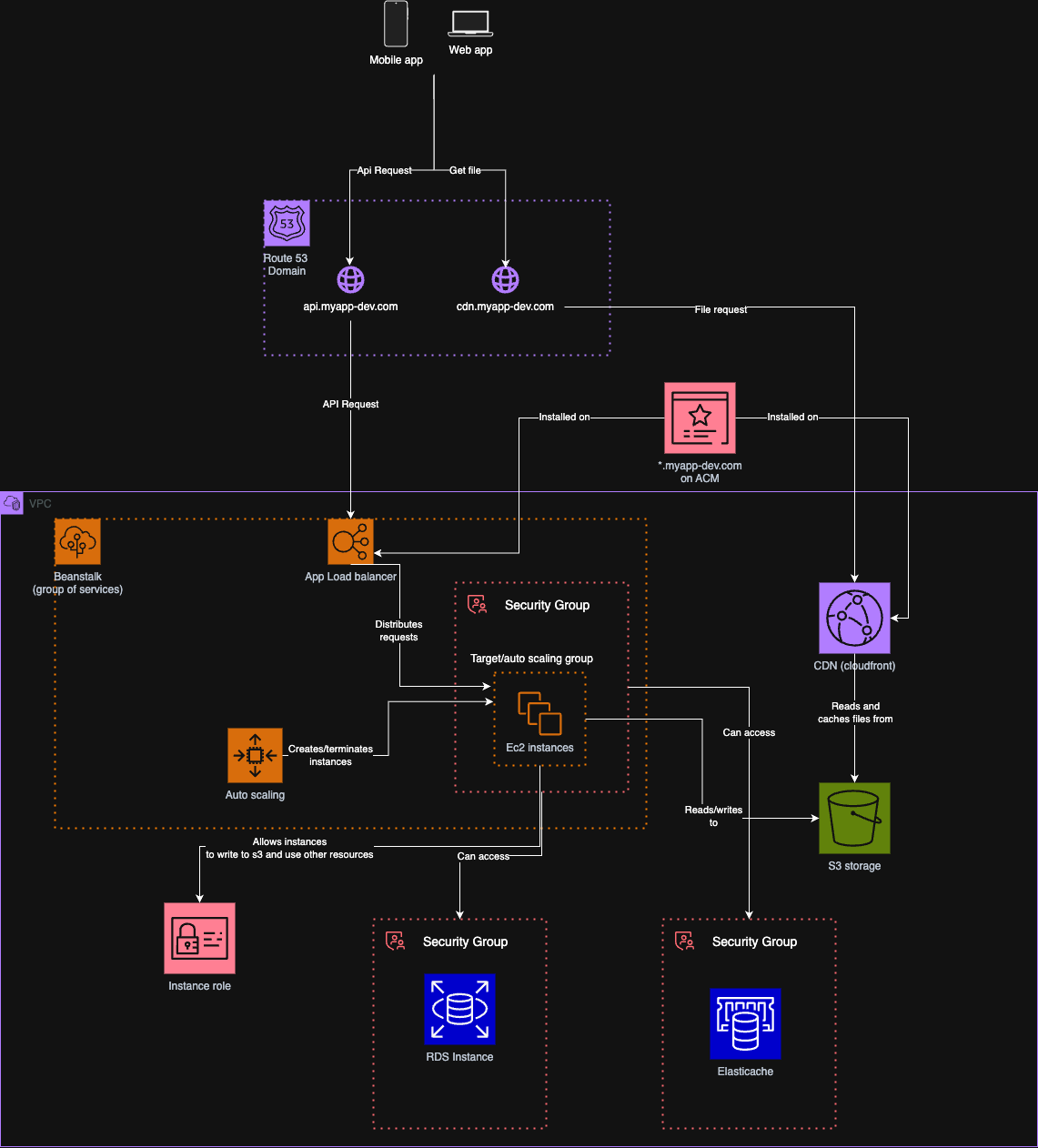
This diagram illustrates the architecture of our application server hosted on AWS. It is designed to ensure scalability, high availability, and secure communication between services.
🧭 Request Flow
-
DNS Resolution
User requests toapi.myapp.comandcdn.myapp.comare resolved via Amazon Route 53, our DNS service. These domains are secured using AWS Certificate Manager (ACM). -
API Traffic
- Requests to
api.myapp.comare routed to an Application Load Balancer (ALB) within a VPC, which distributes incoming traffic to an auto scaling group of EC2 instances. - These instances are provisioned and managed by Elastic Beanstalk, which handles infrastructure orchestration, deployments, and health monitoring.
- Each EC2 instance is granted permissions via an IAM Instance Role to interact with other AWS services like S3, RDS, and ElastiCache.
- Requests to
-
Static Assets and CDN
- Requests for static files (e.g., images, JavaScript, CSS) go to
cdn.myapp.com, which is served via Amazon CloudFront, our content delivery network. - CloudFront caches and serves files from S3, reducing latency and improving performance for end users.
- Requests for static files (e.g., images, JavaScript, CSS) go to
🏗️ Core Components
- Elastic Beanstalk: Manages the application’s environment and EC2 instances, enabling automated scaling and deployments.
- Auto Scaling Group: Dynamically adjusts the number of EC2 instances based on traffic load.
- Application Load Balancer (ALB): Balances traffic across healthy instances in multiple availability zones.
- EC2 Instances: Run the application backend (e.g., API servers), and are secured via a dedicated Security Group.
- RDS Instance: Hosts the relational database PostgreSQL, with access limited to specific instances via Security Groups.
- ElastiCache: Provides low-latency caching via Redis, helping reduce database load and speed up response times.
- S3 Storage: Stores static files and application assets. Read and write access is tightly scoped to instance roles and services.
- CloudFront (CDN): Distributes content globally, fetching and caching assets from S3.
🔐 Security Measures
- Security Groups restrict traffic between resources based on strict ingress/egress rules.
- IAM Instance Role limits access to only the necessary AWS resources for EC2 instances.
- TLS Certificates via ACM provide HTTPS encryption for public domains.
This setup enables us to maintain a clean separation of concerns, while leveraging AWS-native scalability, observability, and cost-efficiency.